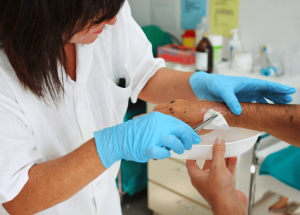
Proper wound management is critical in healthcare, especially for professionals working with vulnerable groups such as the elderly and individuals with disabilities. Understanding and applying the core principles of wound management can significantly improve patient outcomes. Here are the five fundamental principles that guide effective wound care.
1. Assessment and Reassessment
The initial step in wound management involves a thorough assessment of the wound and the patient’s overall health. This includes evaluating the wound size, depth, type, location, and signs of infection. Equally important is assessing patient factors that could influence healing, such as nutritional status, comorbidities, and medication. Continuous reassessment is crucial to monitor healing progress and adapt care plans as needed.
2. Cleaning and Debridement
Cleaning the wound is essential to prevent infection and promote healing. The use of appropriate solutions and techniques ensures the removal of contaminants and dead tissue. Debridement, the process of removing non-viable tissue, is vital for reducing the risk of infection and creating a healthy environment for new tissue growth. This principle underscores the importance of maintaining a clean wound bed to facilitate healing.
3. Moisture Balance
Maintaining an optimal moisture balance is key to wound healing. A moist wound environment promotes cell migration, enhances epithelialisation, and reduces the risk of wound infection. However, excessive moisture can lead to maceration and delayed healing. Selecting the appropriate dressings and changing them at proper intervals are crucial to effectively managing wound moisture.
4. Infection Control
Infection can significantly impede wound healing and lead to complications. Implementing strict infection control measures, including hand hygiene, using sterile techniques during dressing changes, and applying antimicrobial dressings when needed are fundamental practices. Recognising signs of infection early and initiating appropriate treatment are vital components of effective wound management.
5. Patient-Centered Care
The patient’s needs, preferences, and comfort should always be at the forefront of wound management decisions. This involves educating patients and their families about the care plan, addressing pain management, and considering the patient’s lifestyle and mobility in care decisions. Engaging patients in their care promotes adherence to treatment plans and improves overall satisfaction with the care process.
Conclusion
These five principles form the foundation of effective wound management. For healthcare professionals, especially those working in the aged care and disability sectors, integrating these principles into practice is essential for promoting healing and improving patient outcomes. At Colbrow Care, our clinicians and carers undergo continued professional development, ensuring they are well-prepared to provide high-quality wound care in their professional roles.